https://cplusplus.com/reference/map/map/
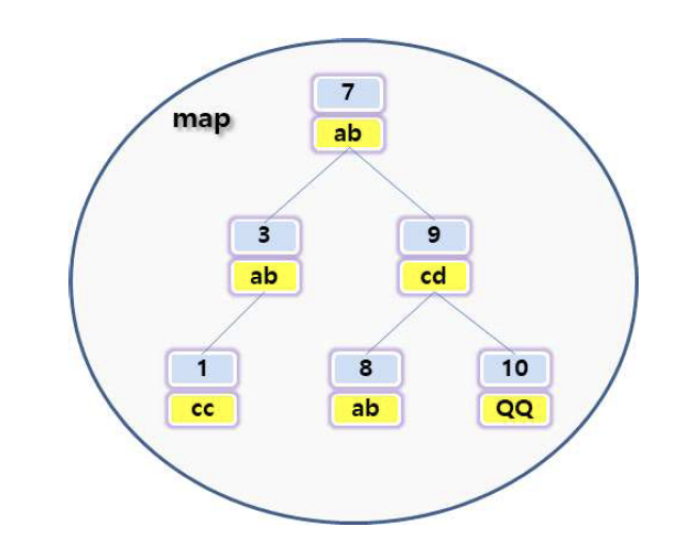
map의 주요 특징
map은 대표적인 연관 컨테이너이자 노드 기반 컨테이너이다.
그래서 특정 정렬 기준으로 원소(key)가 자동 정렬되며 연관 컨테이너(set, multiset, map, multimap)는 모두 같은 인터페이스의 멤버 함수를 제공한다. set의 원소는 key만으로 이뤄지지만 map의 원소는 key와 value의 쌍(pair 객체)으로 이뤄진다. (key와 value의 유형은 서로 다를 수 있으며, value_type으로 그룹화 된다.)
map은 [] 연산자(operator[])를 이용해 원소(key, value)를 추가하거나 key에 매핑된 value의 참조를 반환할 수 있다. map은 set처럼 연관 컨테이너이므로 컨테이너 앞, 뒤에 추가하거나 제거하는 멤버 함수류를 제공하지 않으며 원소를 참조하는 front()와 back() 멤버 함수도 제공하지 않는다.
연관 컨테이너의 핵심은 빠른 원소 찾기(검색)이며 균형 이진 트리를 이용한 로그 시간 검색 복잡도를 보장한다.
map의 매핑된 값은 괄호 연산자를 사용하여 해당 키로 직접 액세스할 수 있다.
맵 컨테이너는 일반적으로 unordered_map 컨테이너보다 키로 개별 요소에 액세스하는 속도가 느리지만, 순서에 따라 하위 집합에 직접 반복할 수 있다.
맵은 일반적으로 이진 검색 트리로 구현된다.
map의 템플릿 형식
멤버 타입
- key_type : 첫 템플릿 파라미터(key)
- mapped_type : 두번째 템플릿 파라미터(T)
- value_type : pair<const key_type, mapped_type>
- key_compare : 세번째 템플릿 파라미터(Compare)
value_compare : 요소 비교하기 위한 중첩 함수 클래스
https://cplusplus.com/reference/map/map/value_comp/
첫 번째 요소의 키가 두 번째 요소보다 앞에 있는지 여부를 확인하기 위해 두 요소를 비교하는 데 사용할 수 있는 비교 개체를 반환한다.
반환된 비교 개체는 멤버 유형 map::value_compare의 개체로, 내부 비교 개체를 사용하여 적절한 비교 함수 클래스를 생성하는 중첩 클래스이다.
template <class Key,class T,class Compare,class Alloc> class map<Key,T,Compare,Alloc>::value_compare {// in C++98, it is required to inherit binary_function<value_type,value_type,bool>friendclass map; protected: Compare comp; value_compare (Compare c) : comp(c) {}// constructed with map's comparison objectpublic: typedefbool result_type; typedef value_type first_argument_type; typedef value_type second_argument_type; booloperator() (const value_type& x,const value_type& y)const { return comp(x.first, y.first); } }binary_function
https://cplusplus.com/reference/functional/binary_function/?kw=binary_function
template <class Arg1, class Arg2, class Result> struct binary_function;
표준 이진 함수 개체에 대한 기본 클래스이다. 일반적으로 함수 객체는 멤버 함수 operator()가 정의된 클래스의 인스턴스이다.
이 멤버 함수는 객체를 일반 함수 호출과 동일한 구문으로 사용할 수 있게 하므로 일반 함수 유형이 예상 될 때 해당 유형의 템플릿 매개 변수로 사용할 수 있다.
template <class Arg1,class Arg2,class Result> struct binary_function { typedef Arg1 first_argument_type; typedef Arg2 second_argument_type; typedef Result result_type; };
- allocator_type : 네번째 템플릿 파라미터(Alloc)
- reference : allocator_type::reference
- const_reference : allocator_type::const_reference
- pointer : allocator_type::pointer
- const_pointer : allocator_type::const_pointer
- iterator : a bidirectional iterator to value_type
- const_iterator : a bidirectional iterator to const value_type
- reverse_iterator : reverse_iterator<iterator>
- const_reverse_iterator : reverse_iterator<const_iterator>
- difference_type : 부호있는 integral타입 : iterator_traits<iterator>::difference_type
- size_type : 차이의 음이 아닌 값을 나타낼 수 있는 부호 없는 integral타입
기본 멤버 함수 ( 생성자, 소멸자, 대입연산자)
- default constructor
explicit map (const key_compare& comp = key_compare(), const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
빈 컨테이너이다.
- range constructor
template <class InputIterator> map (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const key_compare& comp = key_compare(), const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
각 요소가 해당 범위의 해당 요소로 구성된 상태에서 [첫 번째, 마지막] 범위만큼 많은 요소로 컨테이너를 구성한다.
- copy constructor
map (const map& x);
x의 각 요소 복사본을 사용하여 컨테이너를 구성한다.
- destructor
~map();
모든 컨테이너 요소가 파괴되고 맵에 의해 할당된 모든 스토리지 용량이 할당 해제된다.
- operator=
map& operator= (const map& x);
x의 모든 요소를 컨테이너로 복사하여 크기를 변경한다.
Iterator
- begin
- end
- rbegin
- rend
- cbegin
- cend
- crbegin
- crend
Capacity
- empty
- size
- max_size
Element access
- operator[]
mapped_type& operator[] (const key_type& k);
k가 컨테이너에 있는 요소의 키와 일치하면 함수는 매핑된 값에 대한 참조를 반환합니다
이 함수에 대한 호출은 다음과 같습니다:
(*((this->insert(make_pair(k,mapped_type()))).first)).
Modifiers
- Insert
single elementpair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& val);with hintiterator insert (iterator position, const value_type& val);rangetemplate <class InputIterator> void insert (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);- Erase
(1)void erase (iterator position);(2)size_type erase (const key_type& k);(3)void erase (iterator first, iterator last);- swap
void swap (map& x);
- clear
void clear();
Observers
key_compare key_comp() const;
Return key comparison object
value_compare value_comp() const;
Return value comparison object
Operations
iterator find (const key_type& k);const_iterator find (const key_type& k) const;
Get iterator to element
size_type count (const key_type& k) const;
Count elements with a specific key
iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k); const_iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k) const;
Return iterator to lower bound
iterator upper_bound (const key_type& k); const_iterator upper_bound (const key_type& k) const;
Return iterator to upper bound
pair<const_iterator,const_iterator> equal_range (const key_type& k) const; pair<iterator,iterator> equal_range (const key_type& k);
Get range of equal elements
Uploaded by N2T
